- CodeCraft by Dr. Christine Lee
- Posts
- The Swiss Army Knife for Data Scientists
The Swiss Army Knife for Data Scientists
Python NumPy

|
Introduction to NumPy
NumPy (Numerical Python) is an open-source Python library that plays a crucial role in scientific computing, data analysis, and machine learning. It provides powerful tools for working with arrays, matrices, and mathematical functions.
Here are some key features of NumPy with examples:
1. Arrays (ndarray)
The core data structure in NumPy is the ndarray (N-dimensional array).
An ndarray can store elements of the same data type efficiently.
Unlike Python lists, which can contain mixed data types, ndarrays are homogeneous.
These arrays are essential for numerical computations and data manipulation.
Example:
import numpy as np
# Create a 1-D array
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print(arr)

1-D Array
2. Vectorized Operations
NumPy allows you to perform element-wise operations on arrays without explicit loops.
Vectorized operations are more efficient and concise than traditional Python loops.
For example, you can add, subtract, multiply, or divide entire arrays at once.
Example:
import numpy as np
# Element-wise addition
arr1 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
arr2 = np.array([10, 20, 30])
result = arr1 + arr2
print(result)
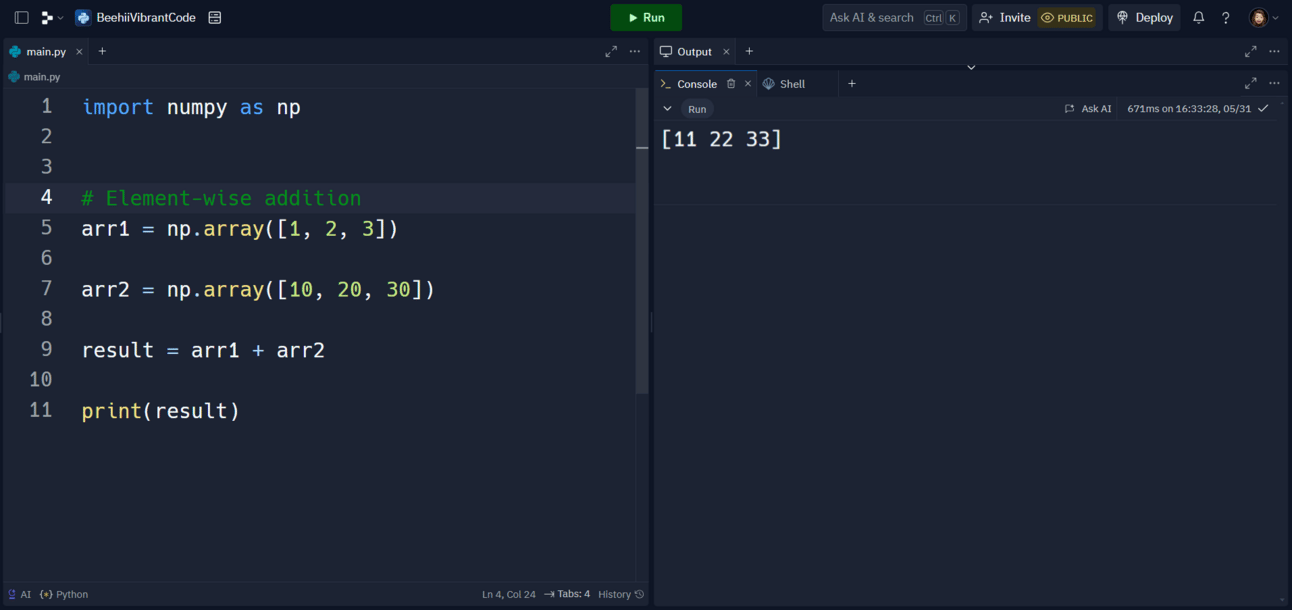
Element-wise operations
3. Broadcasting
Broadcasting enables operations on arrays with different shapes.
When performing operations between arrays, NumPy automatically adjusts their shapes to make them compatible.
This makes code more readable and avoids unnecessary loops.
Example:
import numpy as np
# Broadcasting a scalar to an array
scalar = 5
arr3 = np.array([1, 2, 3])
result2 = arr3 + scalar
print(result2)
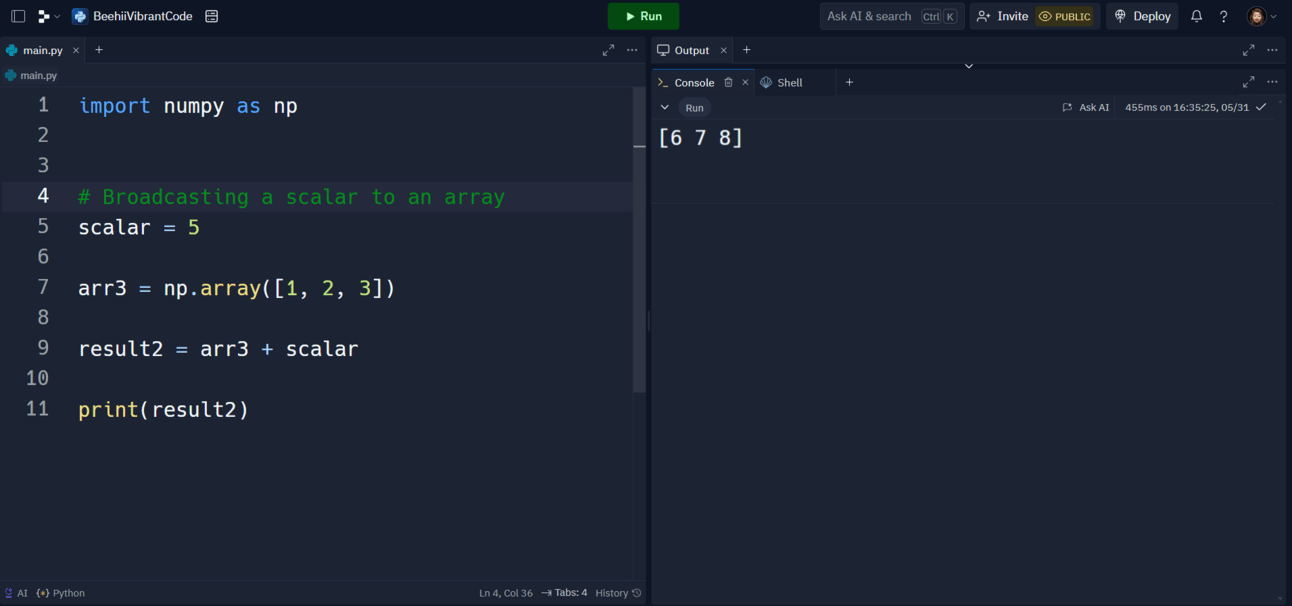
Broadcasting
4. Mathematical Functions
NumPy provides a vast array of mathematical functions:
Trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan)
Exponential and logarithmic functions
Statistical functions (mean, median, standard deviation)
Linear algebra operations (matrix multiplication, eigenvalues, etc.)
Example:
import numpy as np
# Trigonometric function
angles = np.array([0, np.pi / 2, np.pi])
sine_values = np.sin(angles)
print(sine_values)

Trigonometric Function - sin
5. Integration with Other Libraries
NumPy seamlessly integrates with other scientific libraries like SciPy, Matplotlib, and Pandas.
It serves as the foundation for many data science and machine learning tools.
|
Summary
NumPy, short for Numerical Python, is a fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It provides support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a collection of mathematical functions to operate on these arrays efficiently.
NumPy's capabilities are essential for performing a wide range of tasks, from basic array manipulation to complex linear algebra operations. It serves as the backbone for many scientific libraries in Python, including SciPy, pandas, and matplotlib, making it a crucial tool for data analysis, machine learning, and numerical computations. Its efficiency and versatility have made it a cornerstone of the Python scientific computing ecosystem.
Ready for More Python Fun?
Subscribe to our newsletter now and get a free Python cheat sheet! Dive deeper into Python programming with more exciting projects and tutorials designed just for beginners.
Explore further, and happy coding! 🚀✨
